Cellular Respiration Takes Place Inside The

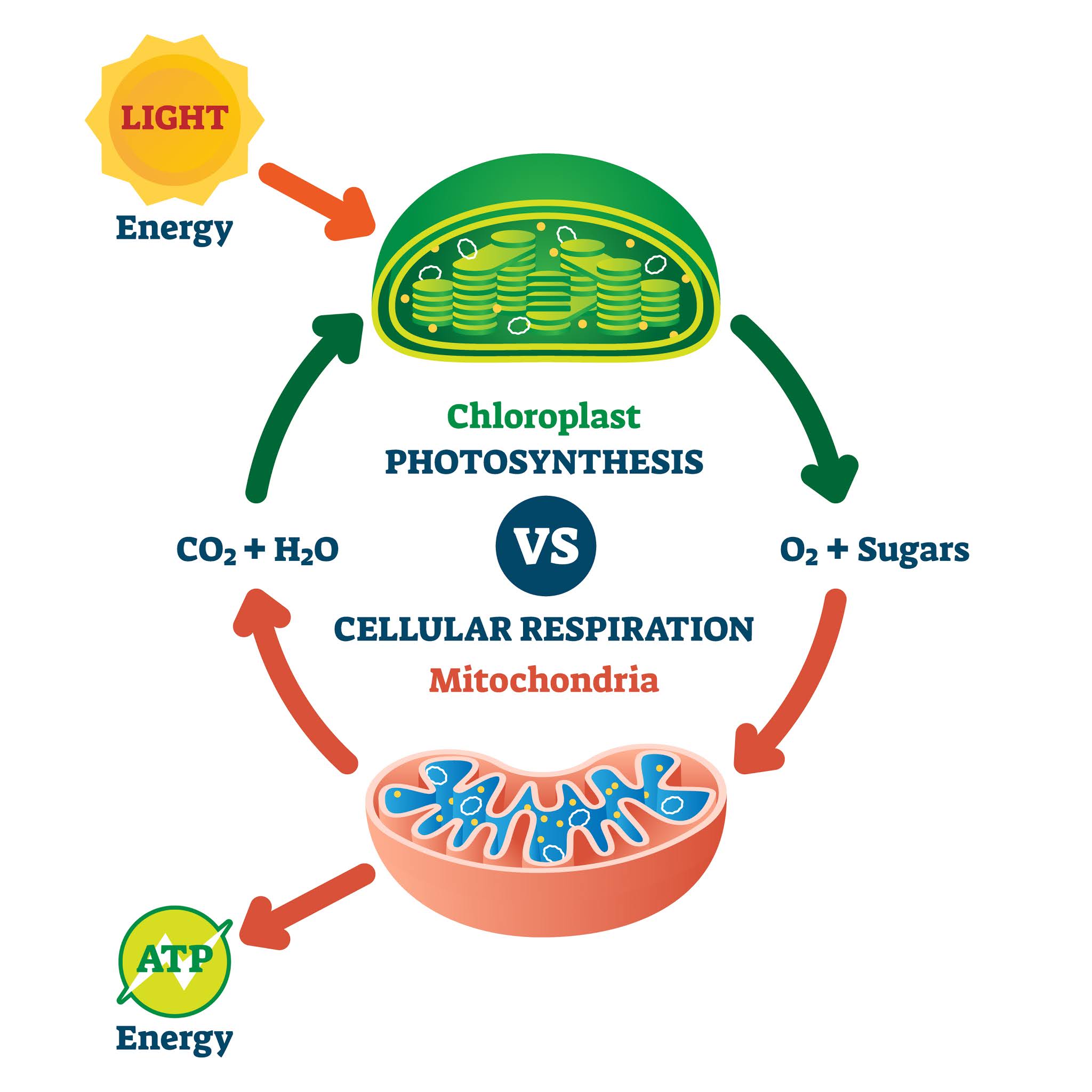
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate atp and then release waste products.
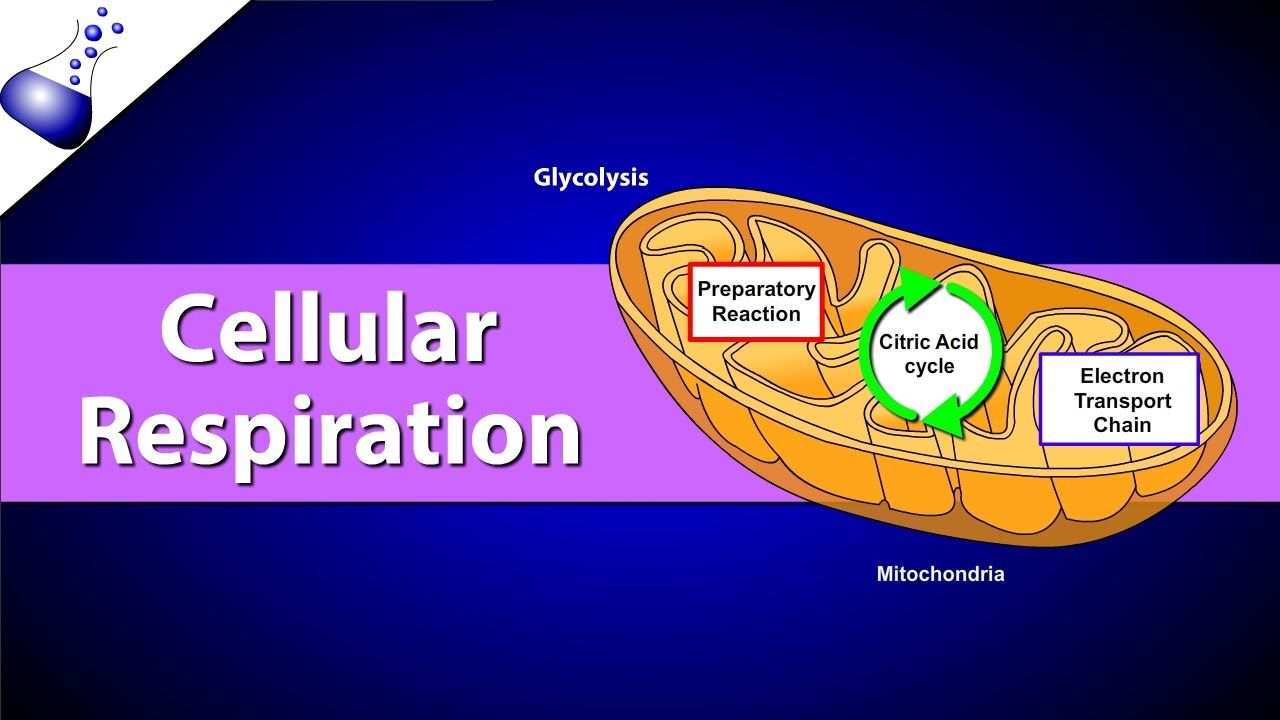
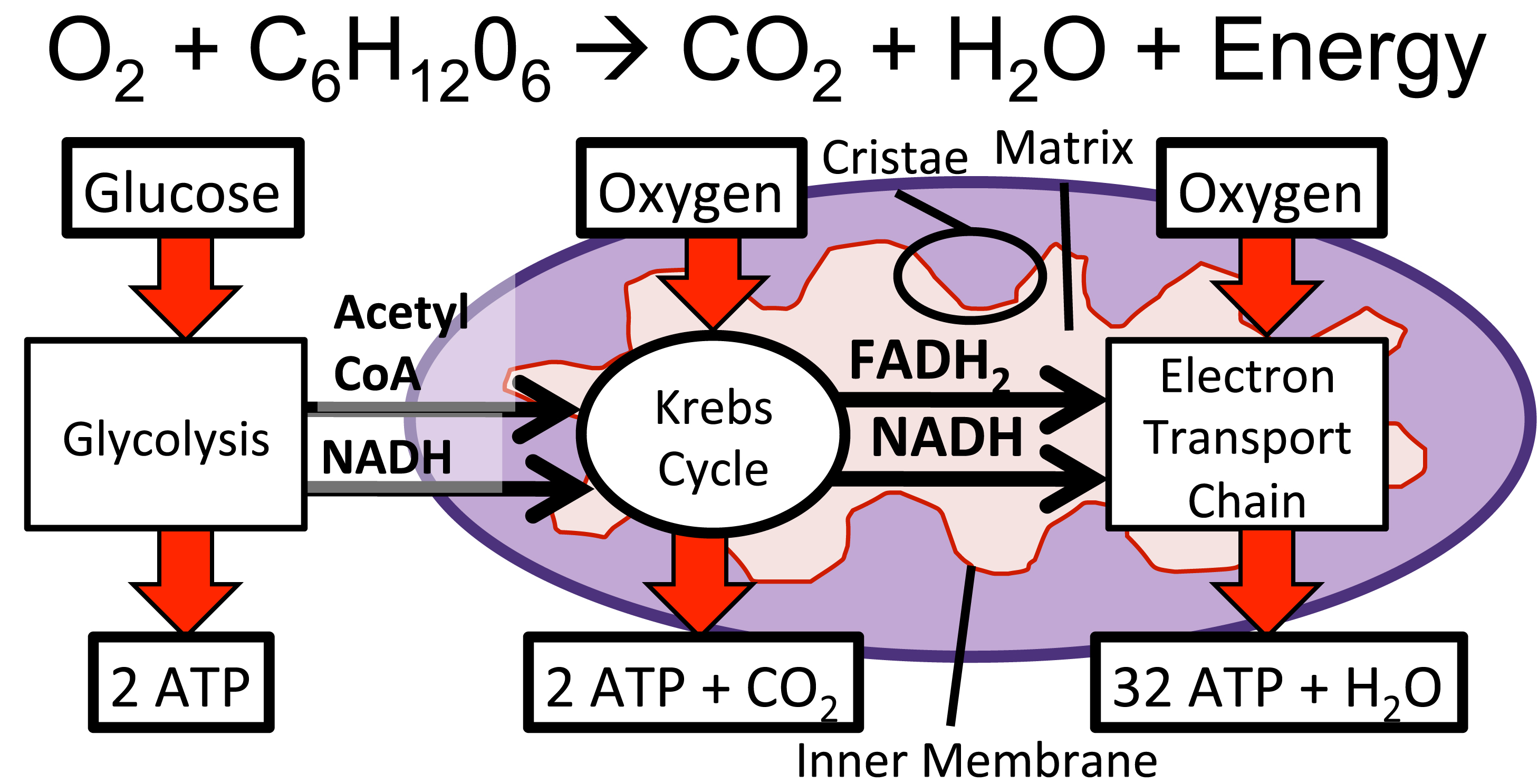
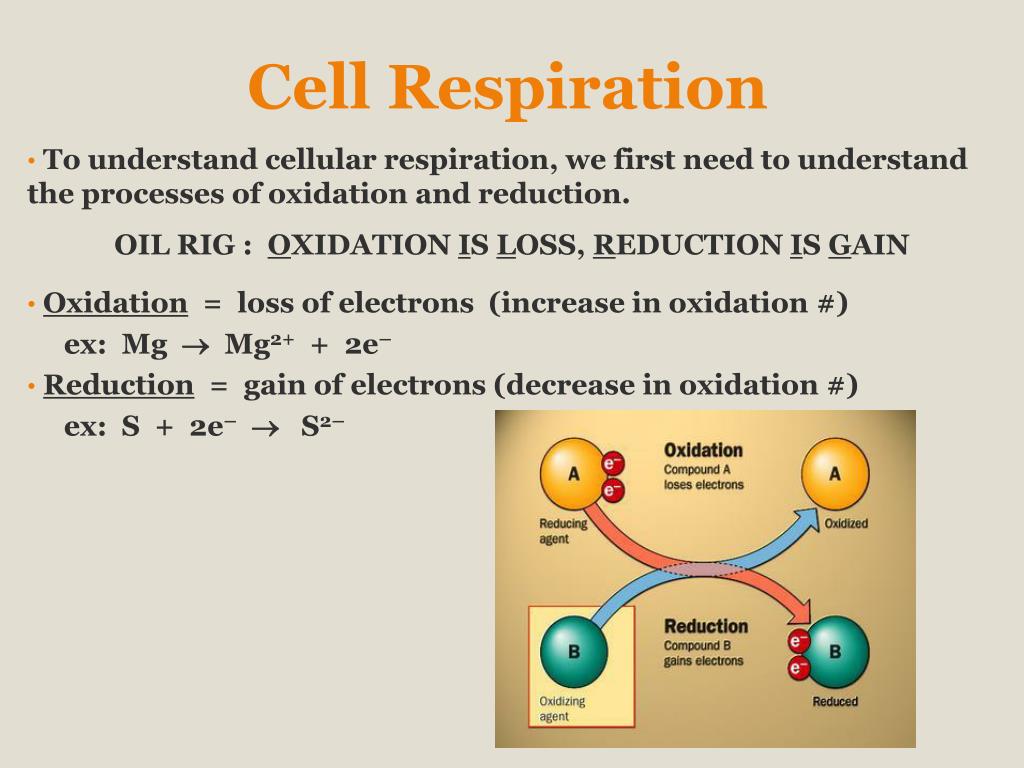
Cellular respiration takes place inside the. Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and electron transportoxidative phosphorylation. The temperature is 25c. Mitochondria the tiny cell organs or organelles in which aerobic cellular respiration takes place are found inside almost all eukaryotic cells.
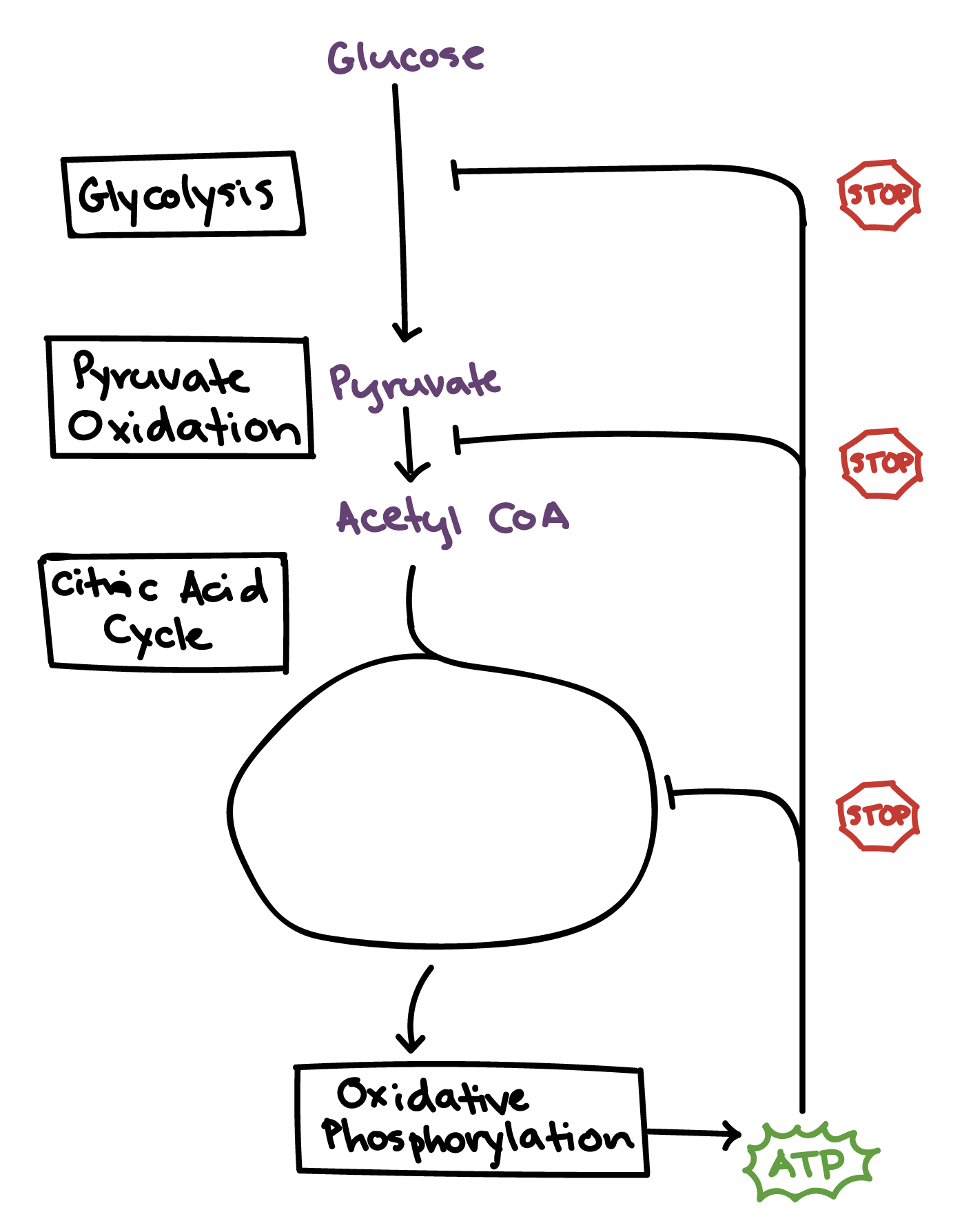
Cell respiration takes place inside the cell organelle called golgi complex lysosome mitochondria ribosome Mitochondria is known as the power house of the c Grade Cell respiration takes place inside the cell organelle. Cellular respiration occurs inside cells. Cellular respiration that takes place where there is NO oxygen Glycolysis The first step of Cellular Respiration where glucose is broken in half and 2 ATP energy units are released.
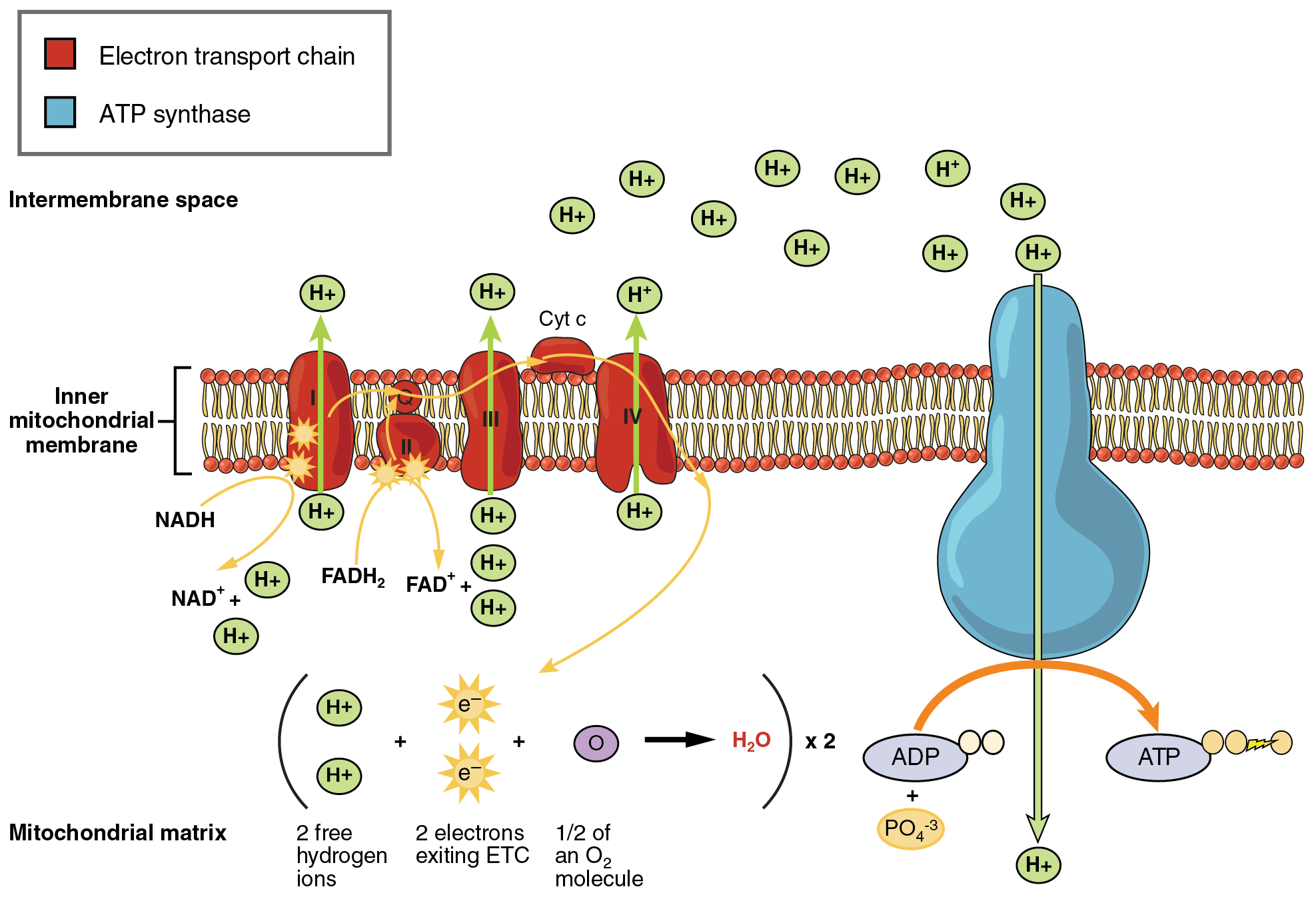
Mitochondria chloroplasts and peroxisomes Tour of a The first stage of cellular respiration called glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm. Inside plant cells glycolysis takes place in the cytosol and the citric acid cycle and oxidative. The energy currency of these cells is ATP and one way to view the outcome of cellular respiration is as a production process for ATP.
More emphasis here will be placed on eukaryotic cells where the mitochondria are the site of most of the reactions. This pathway is anaerobic and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Powerhouse of the cell organelle that is the site of ATP energy production.
Cellular Respiration is the process that takes place in cells to convert food into energy. In order to release the maximal amount of energy the molecules of Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen and Nitrogen which make up our food are stored as a high energy molecule known as ATP or Adenosine Triphosphate. Membrane vesicles containing an internal sodium chloride nacl concentration of 014 m are placed into separate beakers each containing a different solution.
There are three main stages of cellular respiration. There are two halves of glycolysis with five steps in each half. There are two halves of glycolysis with five steps in each half.