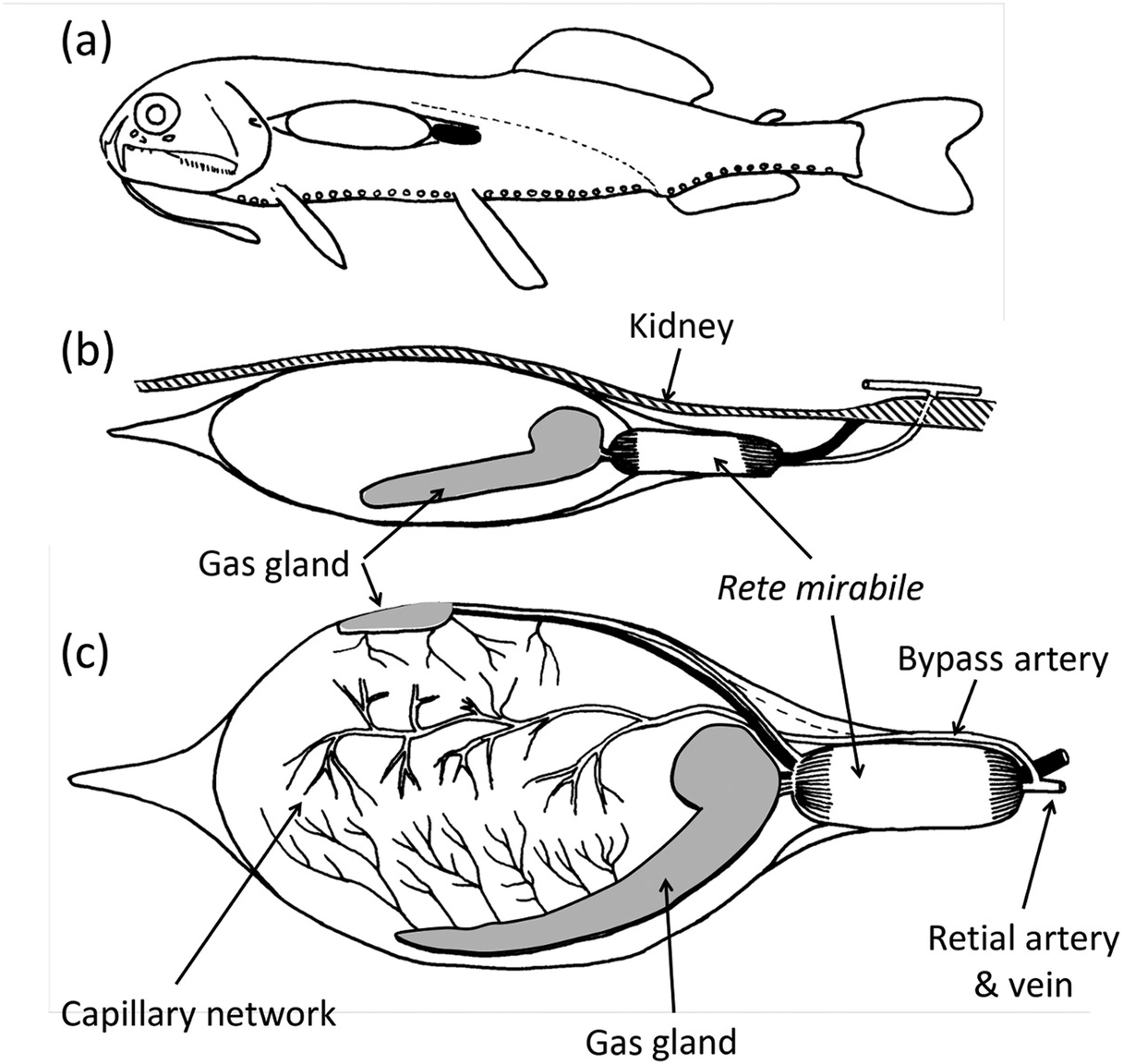
Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations

The abilities of deep-sea animals to tolerate the pressure and temperature conditions of deep-sea habitats are due to pervasive adaptations at the biochemical level.
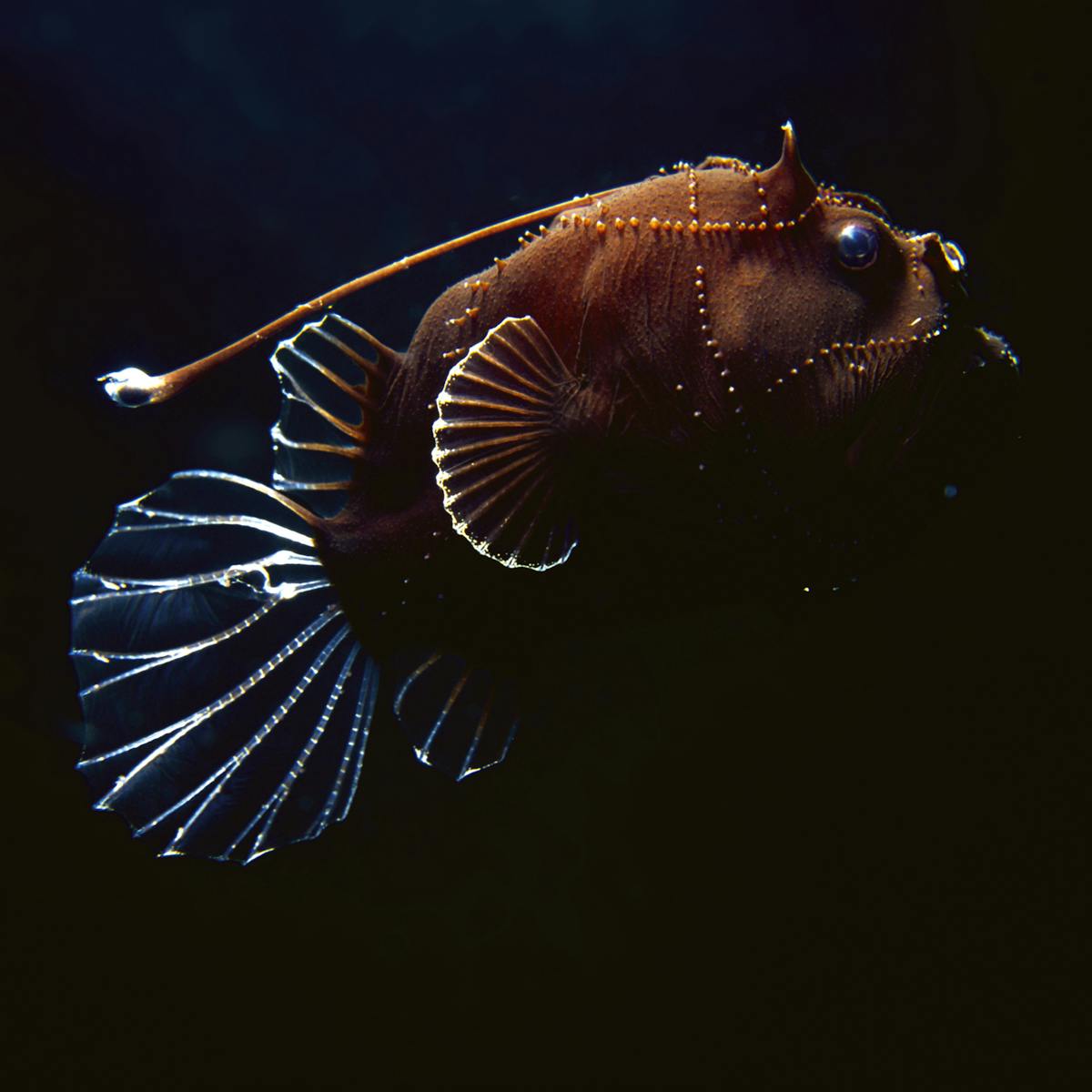
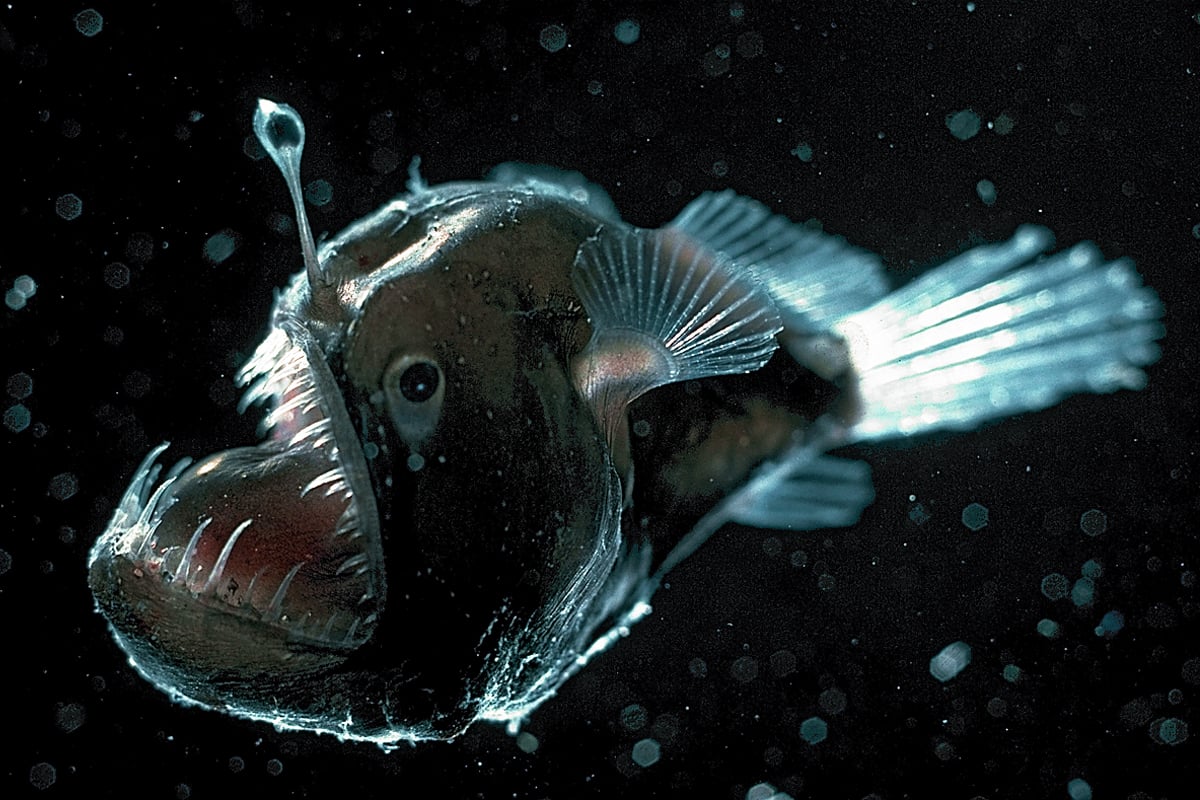
Deep ocean animals adaptations. In anglerfish Linophryne Fig 24 the light is used as a. LS4 - Biological Diversity. Bioluminescent Octopod Bioluminescence is an important adaptation that helps many deep sea animals survive in their dark world.
Have students identify animal adaptations in. Usually lightless sea bottom is referred to as deep sea ie from lower limit of littoral zone 200 metres deep to the ocean floor. They have strong shells that protect them from wave action drying out and the prying beaks of predators.
The deep-sea is cold dark and mysterious but its creatures are known for their amazing adaptations. Deep-sea creatures are animals that live below the photic zone of the ocean. In this lesson students consider the diversity of animals in the deep ocean noting similarities and variations in how animals have adapted to their deep ocean environment.
Contains a chart for students to label the different zones of the ocean as well as a chart to keep track of different animalcreature adaptations in different zones. Deep-sea creatures are animals that live below the photic zone of the ocean. This is often used by animals everywhere for camouflage and protection from predators.
Some of the most amazing adaptations are from ocean animals like sharks jellies starfish stingrays and dolphins. First off the deep ocean is dark because sunlight cant penetrate very far into the water. Food is scarce in much of the deep sea in part because photosynthesis only takes place at the oceans surface where theres sunlight.
Coastal plants need special adaptations to survive. Connection to NGSS -. Watch a recording of this video webinar.