Alpine Tundra Animals Adaptations

Migration and hibernation are examples of behavioral adaptations used by animals in the arctic tundra.
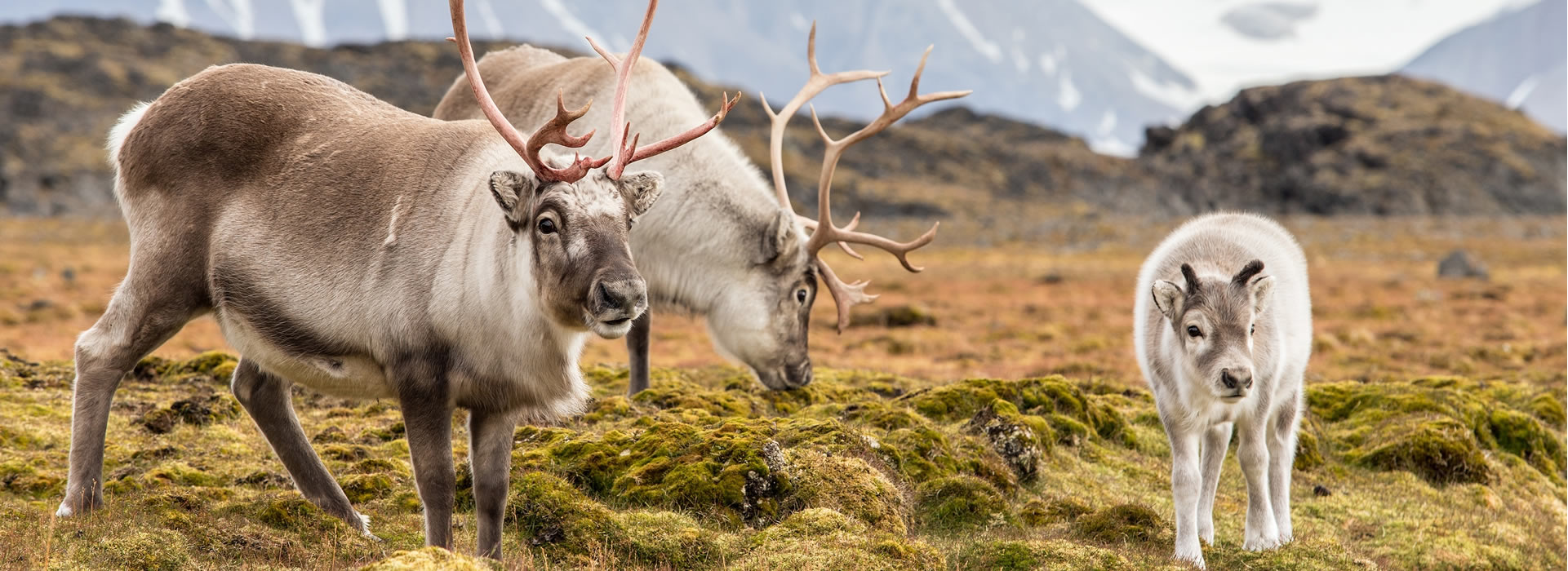
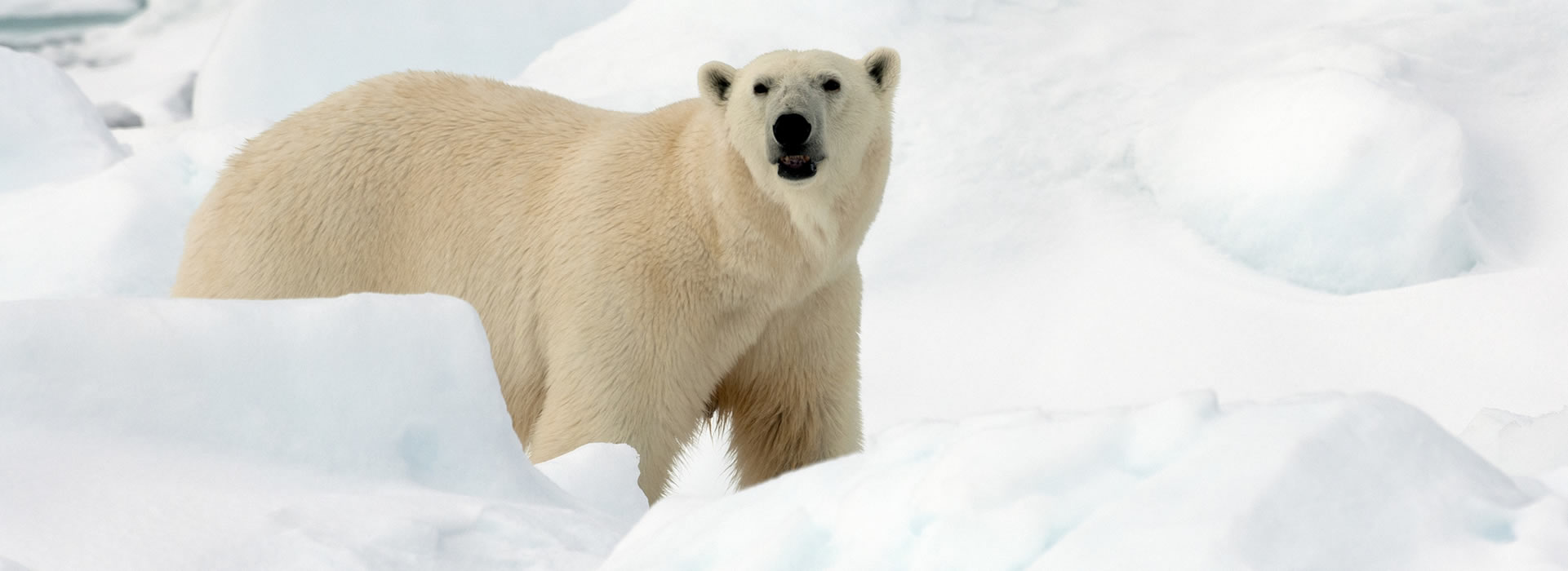
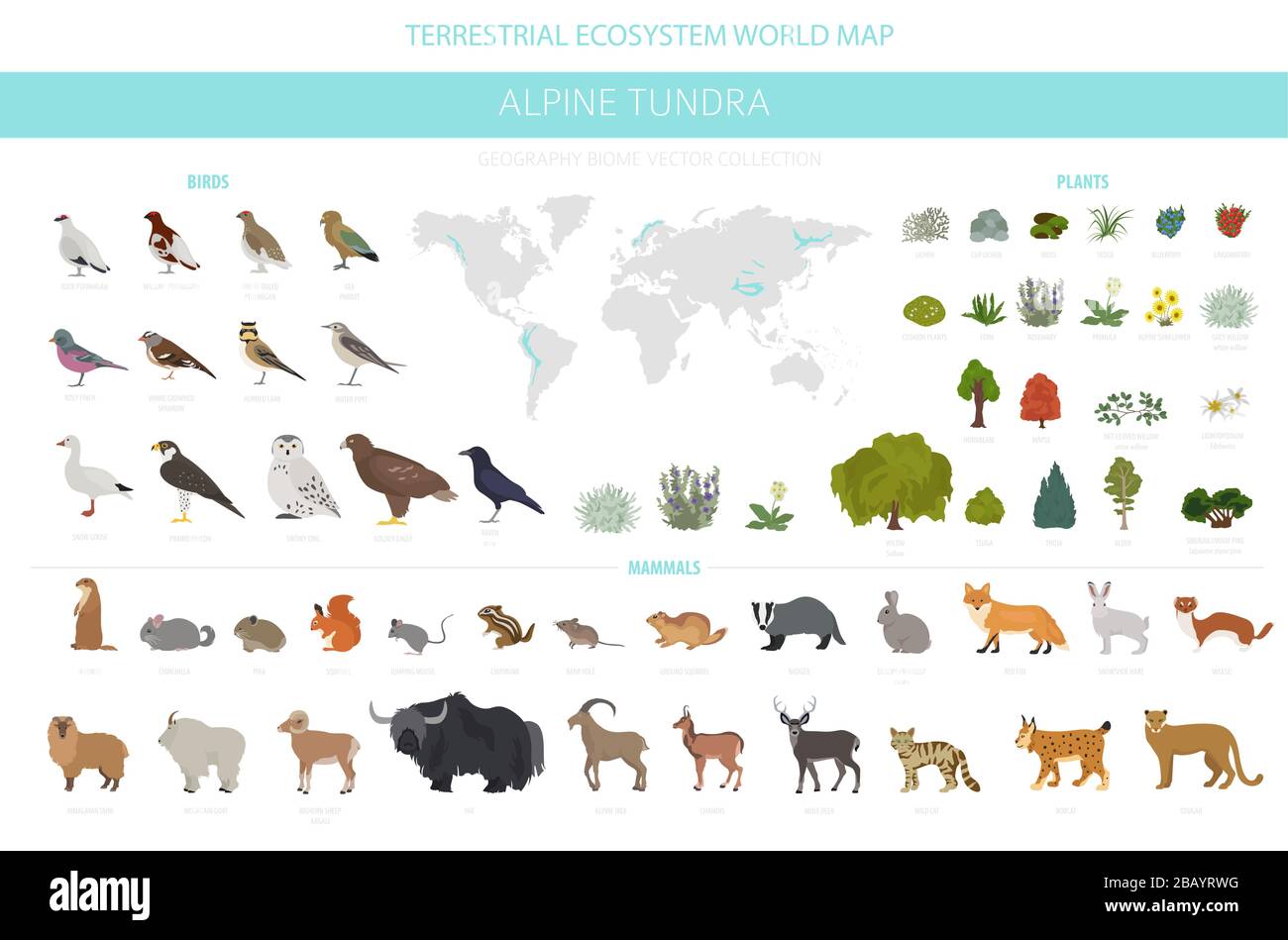
Alpine tundra animals adaptations. Animal adaptations to the the alpine tundra Similar to the arctic tundra we can divide animals that live here into two groups. Animals need shelter and insulation in the tundra. Tundra wildlife includes small mammalssuch as Norway lemmings Lemmus lemmus arctic hares Lepis arcticus and arctic ground squirrels Spermophilus parryii and large mammals such as caribou Rangifer tarandus.
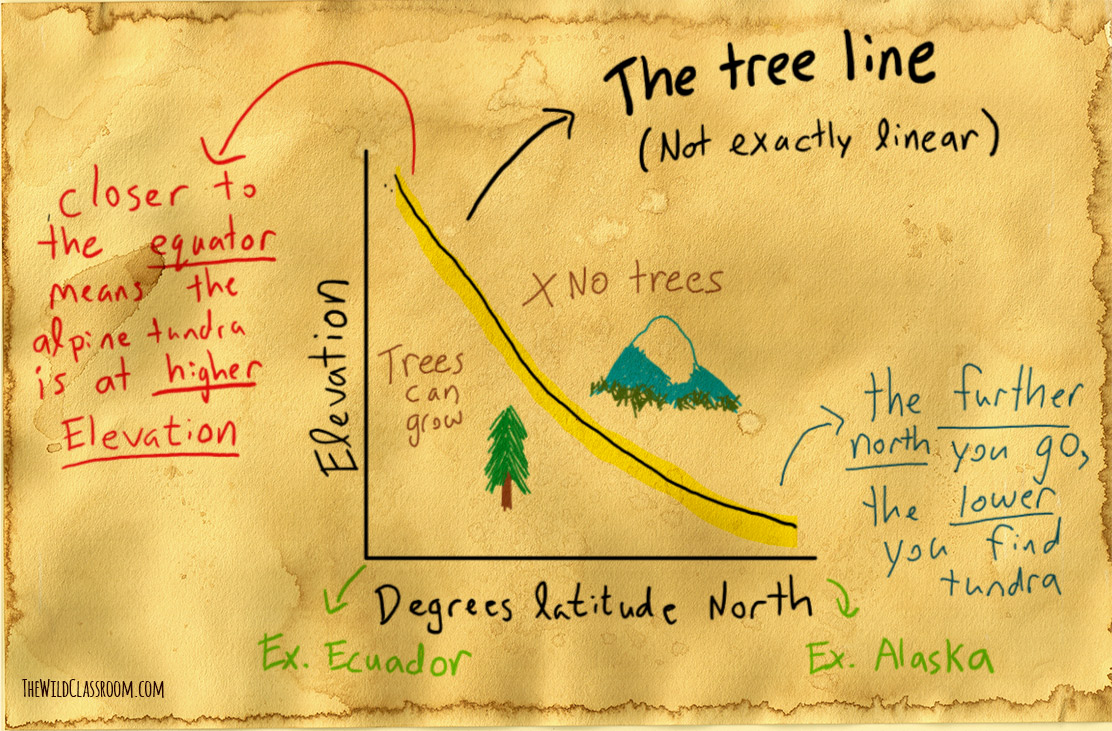
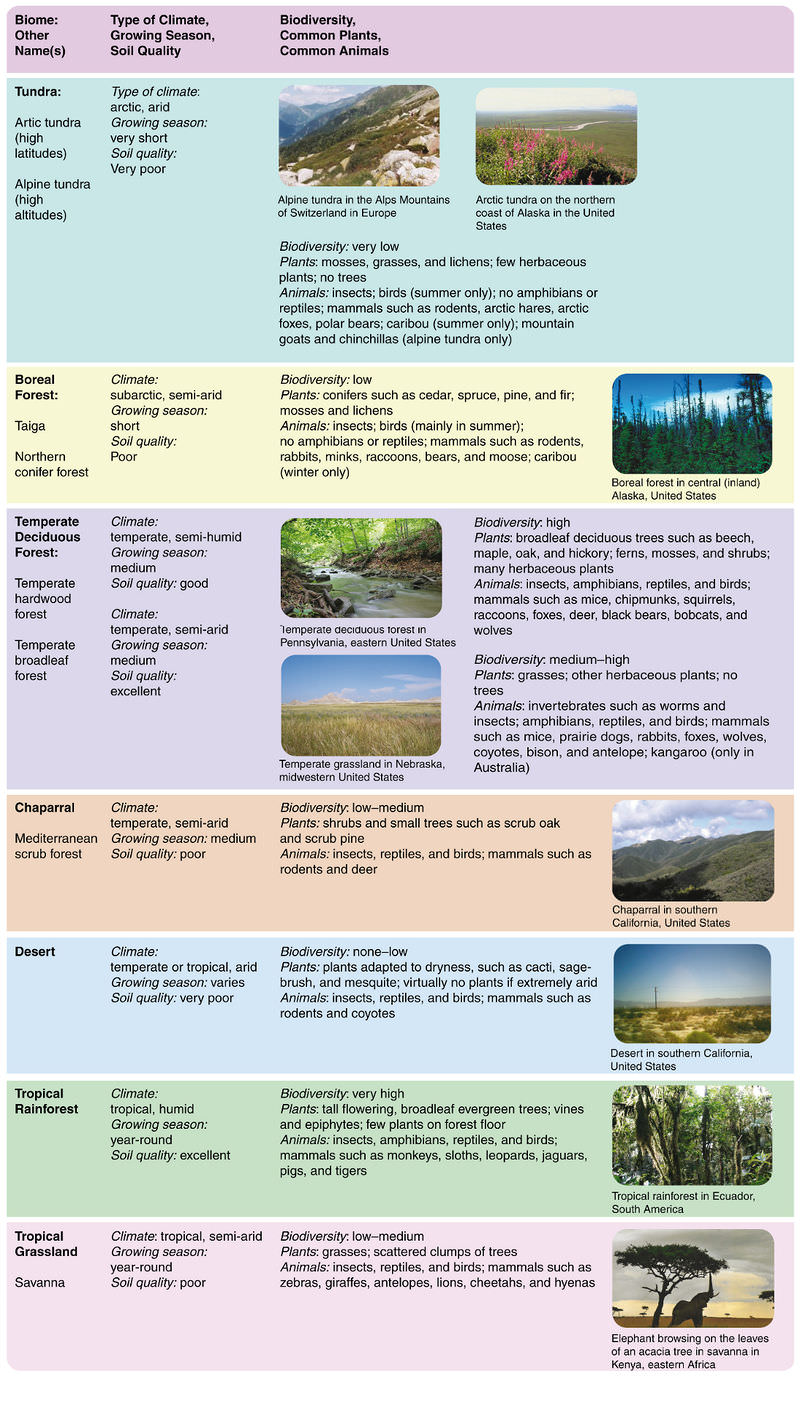
Arctic tundra Antarctic tundra and alpine tundra. In Arctic and alpine tundras the number of species of plants and animals is usually small when compared with other regions yet the number of individuals per species is often high. Climate Location Plants and Animals.
Humans expand their lungs in order to be able to take in more oxygen when they breathe which is scarcer at the higher alpine. Their elevation normally ranges between 10000 feet 3000 meters and the area where a mountains snow line begins. Animal adaptations migration and hibernation are examples of behavioral adaptations used by animals in the arctic tundra.
Adaptations for survival amidst drying winds and cold temperatures may make tundra vegetation seem very hardy but in some respects it remains very fragile. Tread Lightly Repeated footsteps often destroy tundra plants allowing exposed soil to blow away. That are one to two years old.
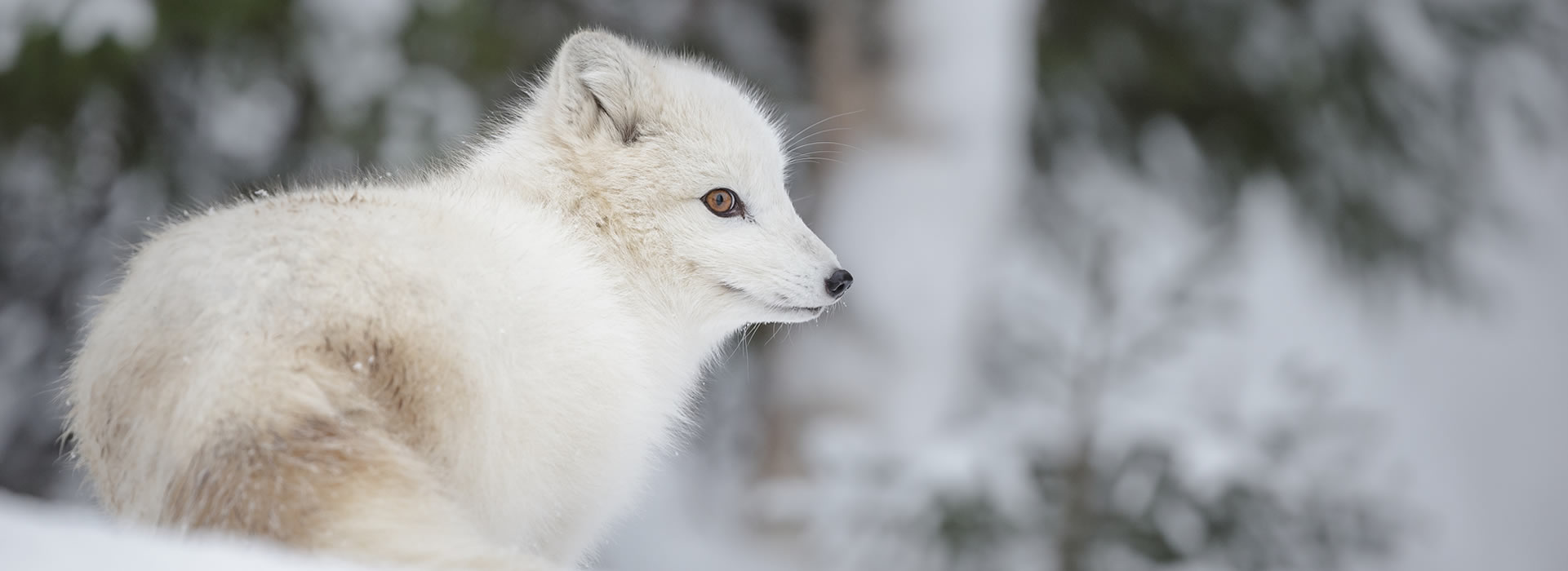
Even humans when living in the alpine biome adapt to the environment. Fluctuating temperatures in brilliant light and in short pe - riods of daylight. Most animal and plant life in this biome have insulation in the way of hair fuzz fur or feathers.
Few alpine animals however contributed directly to the evolution of arctic tundra species because physical barriers prevented the migration of species and because alpine and arctic animals. There are three types of tundra. In summary the tundra is cold with little sunlight and rainfall.